Rabbits
Poultry
Laying hens
Quails
Guinea pigs
Pigs
Ostriches
Sheep and goats
Pigeons
Pheasants
Forest animals
How to recognise a Rabbit´s sex
Determining the sex of a rabbit is a standard breeding procedure that every breeder should be able to perform perfectly. Whereas in the case of young the correct recognition of sex can cause trouble for beginners, in the case of adult rabbits it is straight-forward.
Principles for handling when determining sex
When determining the sex of rabbits, it is necessary to respect the correct technique for handling and fixation – with regard not only to preventing injury to the rabbits, but also to the breeder handling the rabbits.
In breeding practice there are multiple techniques for fixing a rabbit to determine its sex. The simplest solution is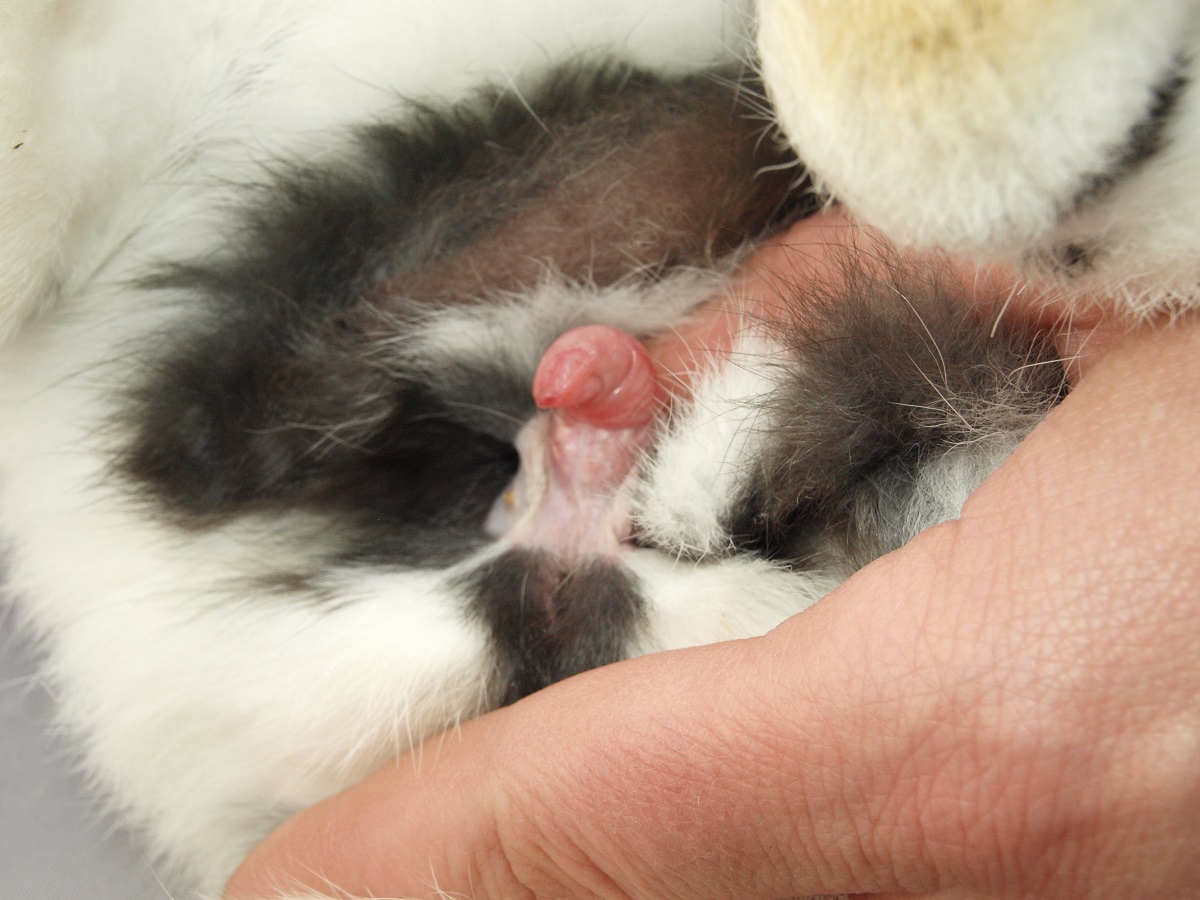
We perform actual determination of the sex in such a manner that we place our index finger at the root of the tail, and with our thumb, gently but surely apply pressure in the area before the external sex organs. The pressure should be enough to reveal the whole external sex organs – in the case of a female it is the vulva, in the case of a male the complete protrusion of the penis. In addition, in the case of a male we see on the sides in the area two non-hairy testicle scrota.
In the older method a rabbit is on a non-slip mat in a natural position and, holding the rabbit by the skin, we lift up its bottom and use our other hand to determine the sex. This older method is, however, unsuitable, as during it the rabbit can more easily escape and primarily by palpation in this position we are not able to uncover any deformities of the external genitals.
Beware of young rabbits!
In the case of young rabbits up to approx. 6 weeks of age, determination of the sex can be quite problematic, but experienced breeders can relatively reliably recognise sex from approximately the third week.
In the case of young rabbits it is necessary to know that they have a relatively large clitoris, which at this age can be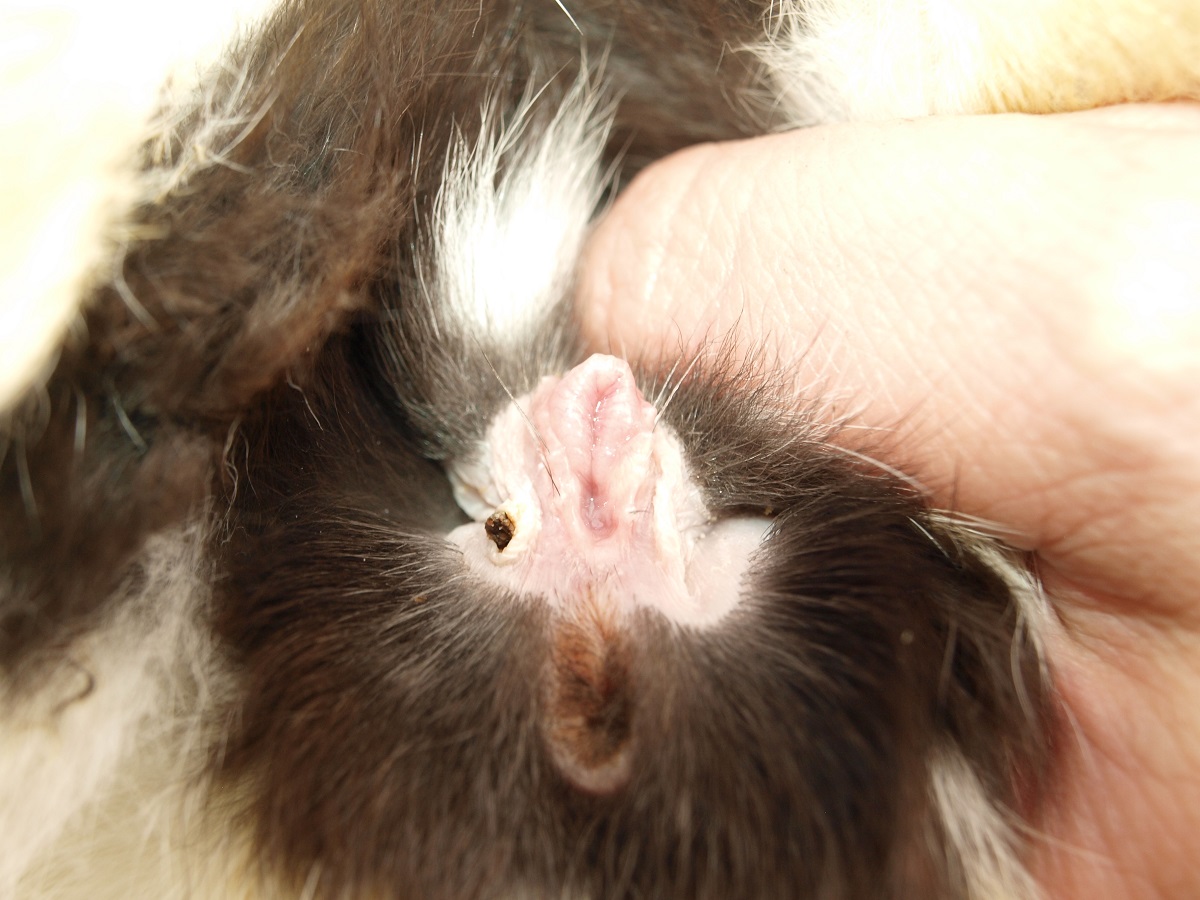 confused with the base of the penis. The scrota of young males develop from approximately the 5th–6th week of age; we can quite reliably determine them from approx. the second month of age. In some bloodlines the development of the scrotum may be somewhat delayed.
confused with the base of the penis. The scrota of young males develop from approximately the 5th–6th week of age; we can quite reliably determine them from approx. the second month of age. In some bloodlines the development of the scrotum may be somewhat delayed.
Male rabbits can retract their testicles
With regard to the possibility of retraction of testicles into the scrota, it is possible that during an examination of the sex we will only see the scrota and the testicles will be in the inguinal canal or in the stomach. After a rabbit calms down, they drop again.
Important information: the development of a visible and normally-built scrotum means that a rabbit has testicles (which may only be temporarily retracted). If a scrotum has not developed, the testicles do not have anywhere do descend to and such male is a cryptorchid. It is a hereditary defect and such individuals are removed from breeding.
Related posts
10. April 2024
Keeping dwarf rabbits as pets is becoming increasingly popular. It does not require a lot of space and is ideal for people who live in smaller homes or apartments. Dwarf rabbits are also very friendly, so it’s no wonder that people are choosing them for this purpose more and more often. As with all animals,…
30. August 2022
In this article we will discuss several rabbit diseases – ear scab, tyzzer’s disease and heat stress.
24. August 2022
In this article we look at two diseases – e.Coli and enterocolitis.
2. August 2022
In this article we look at two common rabbit diseases, myxomatosis and infectious rhinitis.
13. July 2022
In the following article we will discuss rabbit plague – rhd or vhd (viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits).
Related products

RABBIT DWARF
Complete pelleted feed for dwarf rabbits with high digestibility. It contains a high proportion of fibre (high alfalfa and grass cake content) and a reduced sugar and starch content. Contains flaxseed, which has a positive effect on coat quality. Suitable for daily feeding. We recommend providing rabbits with safe fresh water and hay.

RABBIT CHAMPION
Feed for show rabbits, does not include Coccidiostat. A unique mix significantly supports the quality and growth of fur. Serve when moulting and at least two months before the start of the show season.

RABBIT GOLD FORTE
A premium feed mix in an ideal make up for gestating and breast feeding females. For the intensive fattening of rabbits for a period of up to 5 days before slaughter. It supports fast growth, meat content and an excellent state of health. It contains a coccidiostat which lowers the risk of mortality.

RABBIT KLASIK FORTE
Intended for the fattening of rabbits up to a point at least 5 days before slaughter. Suitable for attaining a high meat content and an excellent state of health. Thanks to its Coccidiostat content it lowers the animals mortality.

RABBIT KLASIK
For the final phase of rabbit fattening, a minimum of 5 days before slaughter. It supports high meat content and excellent taste qualities in rabbit meat. Without a coccidiostat.

RABBIT START
For young rabbits from the start of accepting feed to 4-6 weeks after weaning. The feed helps to significantly lower the death rate in the period around weaning. It contains a raised percentage of fibre and less starch. It does not contain a coccidiostat.
