Rabbits
Poultry
Laying hens
Quails
Guinea pigs
Pigs
Ostriches
Sheep and goats
Pigeons
Pheasants
Forest animals
How Long Does a Rabbit Live?
The rabbit belongs to social animals with a medium-term lifespan. This aspect should be taken into account when purchasing the rabbit as a pet animal.
The rabbit and its basic requirements for breeding
When considering which pet to buy, it is always important to study the basic information in the professional literature and the requirements for breeding a particular type of pet animal in advance. This includes not only housing, feeding and care requirements, but also other requirements.
In the case of a rabbit, it should be noted that the average life expectancy of the rabbit under appropriate conditions is medium. During this time it will be necessary to take care of the rabbit correctly. Experience tells us that it is advisable to think carefully with children. They need to be told that they will have to take care of the rabbit day after day under the supervision of their parents. Often, however, there is a gradual decline in the interest of children in the purchased rabbit and care will thus remain mostly / only on the parents.
Average rabbit life expectancy
Rabbits in domestic breeding live 6-8 years on average. Rabbits who have lived up to ten years are also known, but these are really isolated cases. The life of a rabbit in pet breeds can be significantly extended by better care, but genetic equipment plays a crucial role – longevity is regularly inherited in rabbits. Breeding for longevity is one of the current targets for the best rabbit breeders, because having a long-term animal in the care and breeding is always beneficial.
Rabbits are commonly used reproductively until the 4th year, but with good health and milk production, they can be used up to the 5th – 6 years, although a lower number of offspring in the litter and more care of breeders must be expected. Males are reproductively used in breeding until the breeder deems appropriate, usually also up to about 5 to 6 years (excellent breeding males).
Records in the age of rabbits
The current record holder is a dwarf wild-colored rabbit, known as Mick. This rabbit from the USA celebrated his 16th birthday on February 9, 2019 and was recognized by the Guinness Book of Records as the oldest living rabbit on Earth. But he is not the oldest rabbit ever.In this regard, a flopsy rabbit from Tasmania, which was captured in the wild in 1964 and lived to be approximately age 19 years old holds the record!
Taking care of an old rabbit
For a rabbit 5 years old and older, it can be said that it belongs to the age category of seniors. Such rabbits need more individual and regular care than younger rabbits. Older (geriatric) rabbits are much more susceptible to disease and the convalescence period is relatively prolonged, often due to emerging complications. An older rabbit does not require as much movement and exercise as the young rabbit, but just regular, at least short-term movement can be recommended for it because of the beneficial effect on bowel movement. Rabbit seniors are more susceptible to predators or encephalitozoonosis, especially if they are exposed to certain stressors (e.g. summer temperatures, drafts, etc.).
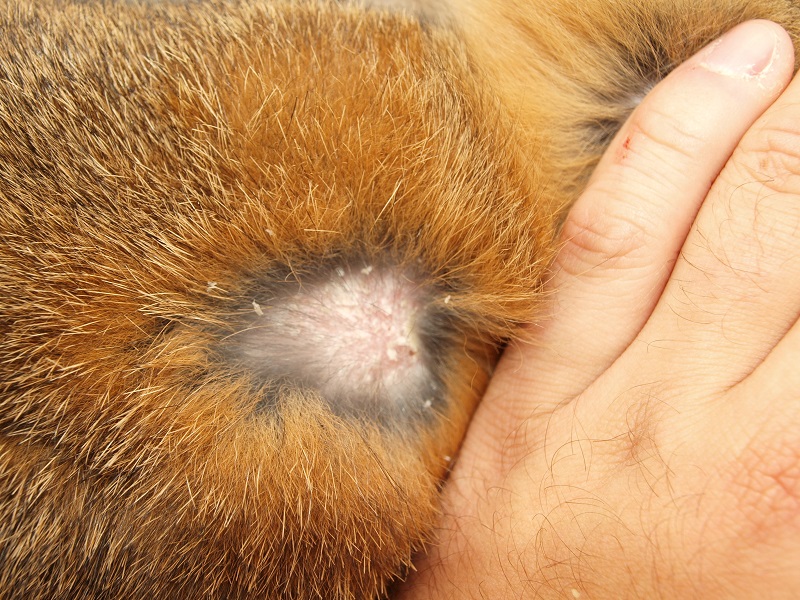
Fig. 1: Prevalence of cheyletiellosis is a common problem in older rabbits
Insufficient fur care, prolonged molting associated with reduced nutritional condition, and walking problems also occur more frequently. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the care of older rabbits in an effort to make them as comfortable as possible.

Fig. 2: In older rabbits, molting is longer
Related posts
10. April 2024
Keeping dwarf rabbits as pets is becoming increasingly popular. It does not require a lot of space and is ideal for people who live in smaller homes or apartments. Dwarf rabbits are also very friendly, so it’s no wonder that people are choosing them for this purpose more and more often. As with all animals,…
30. August 2022
In this article we will discuss several rabbit diseases – ear scab, tyzzer’s disease and heat stress.
24. August 2022
In this article we look at two diseases – e.Coli and enterocolitis.
2. August 2022
In this article we look at two common rabbit diseases, myxomatosis and infectious rhinitis.
13. July 2022
In the following article we will discuss rabbit plague – rhd or vhd (viral haemorrhagic disease of rabbits).
Related products

RABBIT DWARF
Complete pelleted feed for dwarf rabbits with high digestibility. It contains a high proportion of fibre (high alfalfa and grass cake content) and a reduced sugar and starch content. Contains flaxseed, which has a positive effect on coat quality. Suitable for daily feeding. We recommend providing rabbits with safe fresh water and hay.

RABBIT CHAMPION
Feed for show rabbits, does not include Coccidiostat. A unique mix significantly supports the quality and growth of fur. Serve when moulting and at least two months before the start of the show season.

RABBIT GOLD FORTE
A premium feed mix in an ideal make up for gestating and breast feeding females. For the intensive fattening of rabbits for a period of up to 5 days before slaughter. It supports fast growth, meat content and an excellent state of health. It contains a coccidiostat which lowers the risk of mortality.

RABBIT KLASIK FORTE
Intended for the fattening of rabbits up to a point at least 5 days before slaughter. Suitable for attaining a high meat content and an excellent state of health. Thanks to its Coccidiostat content it lowers the animals mortality.

RABBIT KLASIK
For the final phase of rabbit fattening, a minimum of 5 days before slaughter. It supports high meat content and excellent taste qualities in rabbit meat. Without a coccidiostat.

RABBIT START
For young rabbits from the start of accepting feed to 4-6 weeks after weaning. The feed helps to significantly lower the death rate in the period around weaning. It contains a raised percentage of fibre and less starch. It does not contain a coccidiostat.
